
สถาบันห้องปฏิบัติการอ้างอิงแห่งชาติ (สอช.)
ผลงานตีพิมพ์โดดเด่น High Impact Factor ในวารสารวิชาการนานาชาติ ในระดับ Q1-Q2
🆕 สถาบันห้องปฏิบัติการอ้างอิงแห่งชาติ (สอช.) ขอประกาศผลงานตีพิมพ์โดดเด่น Q1-Q2 ประจำปี พ.ศ.2566-2568 ที่นักวิจัยและนักวิทยาศาสตร์ของ สอช.ได้เป็นผู้ร่วมตีพิมพ์ในวารสารวิชาการระดับนานาชาติ (International Publications) ที่มี High Impact Factors ในระดับ Quartile tier 1 และ 2 (Q1 และ Q2) ดังนี้

🧑🔬👩🔬 นส. อุษณีย์ พันธุลาภ ตำแหน่ง นักวิทยาศาสตร์ชำนาญการ
🔬- กลุ่มวิเคราะห์โครงสร้างและพื้นผิว (คพ.) ศูนย์ห้องปฏิบัติการอ้างอิงฟิสิกส์ (ศอฟ.)
📑 ผู้ร่วมวิจัย ลำดับที่ 8
Yue Chen, Ting Wang, Ziwei Yan, Fanrui Zeng, Yingyi Li , Chen Bao, Hua Wang, Usanee Pantulap, Aldo R. Boccaccini, Kai Zheng and Wen Sun, Bioactive glass-induced B cell depletion remodels the osteoimmunological microenvironment to enhance osteogenesis, Acta Biomaterialia, 2025, Vol. 201, p. 648-664
– Impact Factor: 9.6
– Ranking: Q1
– DOI:10.1016/j.actbio.2025.06.001
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S174270612500409X
🧾Abstract
B cells are critical in bone homeostasis, and their dysfunction is linked to various bone disorders. Bioactive glasses (BGs) are known for their immunomodulatory properties and are increasingly utilized in bone regeneration. However, the specific effects of BGs on B cells and their subsequent impact on osteogenesis remain unclear. In this study, we investigated the immunomodulatory effects of three BGs (45S5-BG, 13-93-BG, and B3-Cu-Zn-BG) on B cells. 13-93-BG had minimal effect on the survival of activated B cells, while 45S5-BG induced a noticeable cytotoxic effect on B cells. Notably, B3-Cu-Zn-BG exhibited the highest cytotoxicity towards pathogenic B cells, prompting further investigation into its mechanisms. The ionic dissolution products (IDPs) of B3-Cu-Zn-BG exerted concentration- and time-dependent cytotoxicity on B cells by upregulating the expression of genes associated with the mitochondrial apoptosis pathway and NADPH oxidases. B3-Cu-Zn-BG-derived IDPs elevated reactive oxygen species production in B cells, which induced apoptosis in a concentration-dependent manner. Additionally, when co-cultured with bone marrow stem cells (BMSCs), B3-Cu-Zn-BG-derived IDPs promoted osteoblastic differentiation of BMSCs while selectively targeting and eliminating B cells. To confirm the in vivo osteoimmunomodulatory effects of B3-Cu-Zn-BG-derived IDPs, we employed a human tumor necrosis factor transgenic (TNF-tg) mouse model of rheumatoid arthritis. Intra-articular injection of the IDPs in TNF-tg arthritic mice attenuated bone erosion by reducing B cell aggregates and improving osteoblastic differentiation. This study indicates that B3-Cu-Zn-BG not only induces B cell apoptosis but also promotes osteogenesis, highlighting its potential as a therapeutic strategy for inflammatory bone diseases.

🧑🔬👩🔬 ดร. จรูญ จันทร์สมบูรณ์ ตำแหน่ง รองผู้อำนวยการสถาบันห้องปฏิบัติการอ้างอิงแห่งชาติ (รอง ผอ.สอช.)
🔬- สถาบันห้องปฏิบัติการอ้างอิงแห่งชาติ (สอช.)
📑 ผู้ร่วมวิจัย ลำดับที่ 4
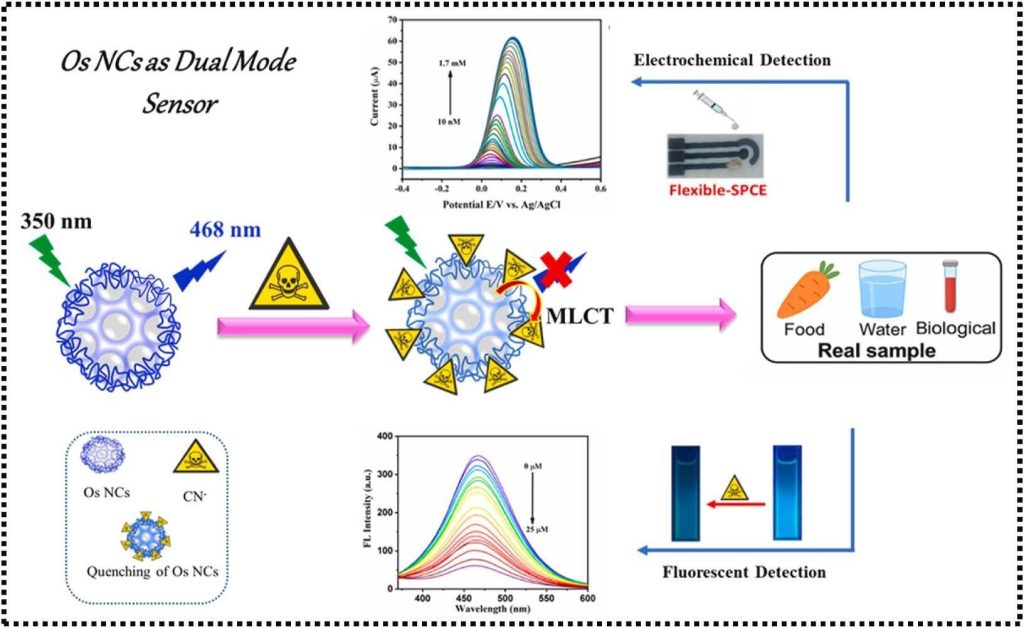
Raheel Akram, S. Lokeswara Reddy, Anila Arshad, Jaroon Junsomboon, Serena Arnaboldi and Jaroon Jakmunee, PEI-capped osmium nanoclusters (Os NCs) for dual-mode fluorescence and electrochemical detection of cyanide: A robust platform for environmental sensing, Talanta, 2025, Vol. 268, Part A, 128667
– Impact Factor: 6.1
– Ranking: Q1
– DOI:10.1016/j.talanta.2025.128667
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0039914025011580
🧾Abstract
Cyanide (CN−), a pervasive and highly toxic industrial pollutant, poses acute environmental and health risks due to its high bioavailability and disruption of cellular respiration. Conventional detection methods often lack sensitivity, portability, or real-time applicability, underscoring the need for advanced sensing technologies. Herein, we report the development of polyethyleneimine (PEI)‐capped osmium nanoclusters (Os NCs) as a dual-mode sensor for highly sensitive fluorescence and electrochemical detection of CN−. The PEI-assisted synthesis yielded biocompatible, solvent-free Os NCs with uniform ultrasmall sizes (2–3 nm, confirmed by TEM) and remarkable stability (up to 3 months) exhibiting with detection limits of 12 nM (fluorescence) and 12.93 nM (electrochemistry), with broad linear ranges of 0.03–24.0 μM and 0.01–200 μM, respectively. The detection mechanism is based on electrostatic interaction between the positively charged amine groups (–NH2) of PEI and the negatively charged CN−, forming a conjugated structure that quenches fluorescence via metal to ligand charge transfer (MLCT) while enhancing electrochemical current. The electrochemical sensor was successfully applied to real samples, including roof tiles leachates, with validation of results by ion chromatography (IC). Additionally, CN− recoveries from spiked food and biological samples ranged from 93.65 to 102.66 % and 89.46–97.43 %, respectively. These results establish Os NCs as a cost-effective, robust platform for sustainable CN− monitoring in environmental and biological matrices.

🧑🔬👩🔬 ดร. พิจิกา มูลอำคา ตำแหน่ง นักวิทยาศาสตร์ชำนาญการ
🔬- กลุ่มวิศวกรรมวัสดุ (วว.) ศูนย์ห้องปฏิบัติการอ้างอิงฟิสิกส์ (ศอฟ.)
📑 ผู้ร่วมวิจัย ลำดับที่ 3
Supada Khonyoung, Jantima Upan, Pijika Mool-am-kha, Jamras Lerdsri, Jaroon Jakmunee and Preeyaporn Reanpang, A rapid and reliable electrochemical determination of 5- hydroxymethylfurfural in honey exploiting nickel oxide nanoparticles modified electrode, Talanta, 2024, Vol. 268, Part 2, 125373
– Impact Factor: 6.1
– Ranking: Q1
– DOI:10.1016/j.talanta.2023.125373
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0039914023011244?via%3Dihub
🧾Abstract
This study presents a novel approach for the rapid and reliable electrochemical determination of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural (5-HMF) in honey using a screen-printed carbon electrode modified with nickel oxide nanoparticles (NiONPs/SPCE). The NiONPs were synthesized using a simple method and characterized using scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). The NiONPs/SPCE demonstrated enhanced sensitivity and selectivity for 5-HMF detection. The electrochemical behavior of 5-HMF on the NiONPs/SPCE was investigated using techniques such as cyclic voltammetry (CV) and square wave voltammetry (SWV). The optimum experimental conditions were obtained including a 5 μL of 5.0 mg/mL NiONPs modifier, the voltammetric response of step potential 15 mV, amplitude 50 mV and frequency 50 Hz in 0.1 M BR buffer pH 13 as supporting electrolyte. The proposed method exhibited a linear relationship between the cathodic peak current and the concentration of 5-HMF in the concentration ranges of 0.5–5.0 ppm, with a limit of detection (LOD) of 0.24 ppm. The selectivity of the NiONPs/SPCE was evaluated by studying potential interferences commonly found in honey samples, and the results demonstrated excellent selectivity for 5-HMF detection. The reproducibility and stability of the NiONPs/SPCE were also assessed, with low relative standard deviations (RSD) obtained for both the cathodic peak current (2.94 %) and long-term stability (3.14 %). The developed NiONPs/SPCE method was successfully applied to the determination of 5-HMF in real honey samples, yielding comparable results to the standard HPLC method. This work showcases the potential of the NiONPs/SPCE as a practical and cost-effective electrochemical sensor for the accurate analysis of 5-HMF in honey samples.

🧑🔬👩🔬 ดร. พิจิกา มูลอำคา ตำแหน่ง นักวิทยาศาสตร์ชำนาญการ
🔬- กลุ่มวิศวกรรมวัสดุ (วว.) ศูนย์ห้องปฏิบัติการอ้างอิงฟิสิกส์ (ศอฟ.)
📑 ผู้ร่วมวิจัย ลำดับที่ 1
Pijika Mool-am-kha, Samuch Phetduang, Nopphakon Phongsanam, Chayada Surawanitkun, Kessarin Ngamdee and Wittaya Ngeontae, A fluorescence biosensor for organophosphorus pesticide detection with a portable fluorescence device-based smartphone, Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 2025, Vol. 327, 125330
– Impact Factor: 4.6
– Ranking: Q2
– DOI:10.1016/j.saa.2024.125330
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1386142524014963?via%3Dihub
🧾Abstract
An innovative fluorescence biosensor was successfully developed to detect organophosphorus pesticide (OPs) by utilizing smartphone technology. The assay relied on the enzymatic activity of alkaline phosphatase (ALP), which facilitated the conversion of L-ascorbic acid 2-phosphate sesquimagnesium salt hydrate (AAP) into L-ascorbic acid (AA). The AA that generated was then reacted with o-phenylenediamine (OPD) to yield a fluorescent marker identified as 3-(1,2-dihydroxyethyl)furo[3,4-b]quinoxalin-1(3H)-one (DFQ). A novel bandpass approach was specifically developed for a smartphone that was integrated with a customized portable fluorescence device to measure the fluorescence emission of DFQ. The device has a unique application that converts the fluorescence intensity into an RGB signal. In the presence of OPs, malathion was chosen as the representative of the OPs substance; the enzymatic activity of the ALP was inhibited, resulting in a decrease in fluorescence intensity, which was proportional to the concentration of malathion. Smartphones can be used to measure fluorescence emission, offering a calibration sensitivity more than 70 times higher than that of conventional spectrofluorometer. The recently developed methodology can be employed to identify malathion within the concentration range of 0.1–1 ppm, with a detection limit of 0.05 ppm. The practical applicability of the method was established using vegetable samples, and the acquired results were in good agreement with those obtained using the standard HPLC approach. This innovative method provides both portability and accuracy, while also exhibiting a notable degree of sensitivity in detecting trace amounts of OPs.

🧑🔬👩🔬 ดร. สุรีรัตน์ ยอดเถื่อน ตำแหน่ง นักวิทยาศาสตร์ชำนาญการ
🔬- กลุ่มวิเคราะห์โครงสร้างและพื้นผิว (คพ.) ศูนย์ห้องปฏิบัติการอ้างอิงทางฟิสิกส์ (ศอฟ.)
📑 ผู้ร่วมวิจัย ลำดับที่ 3
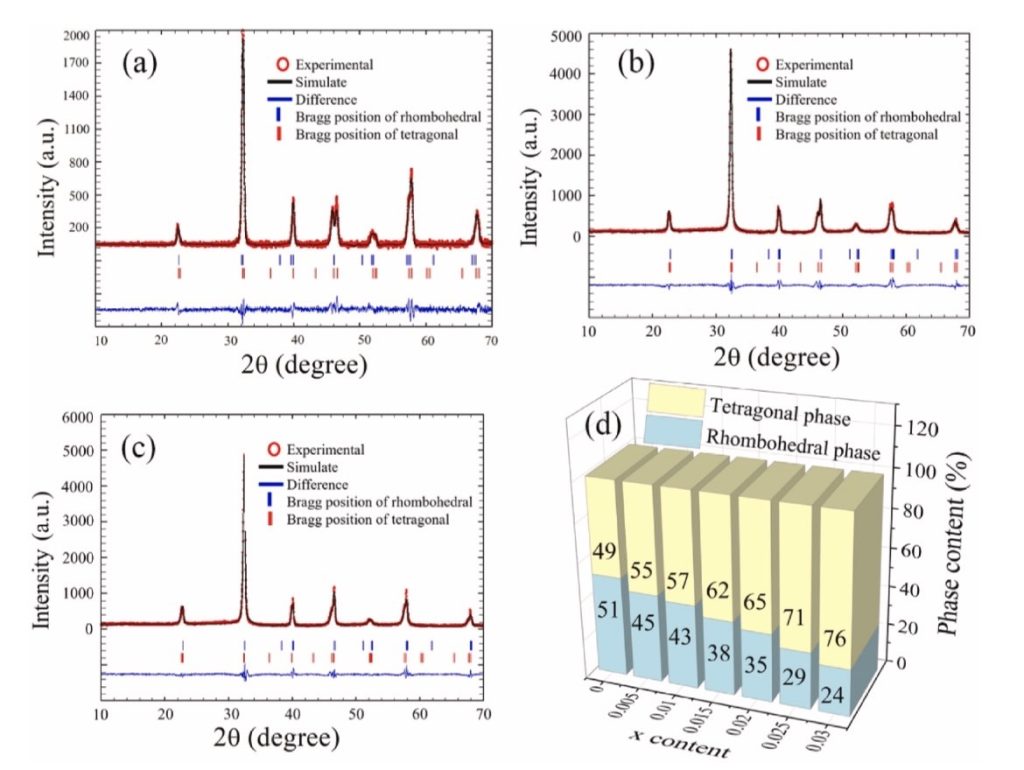
C. Kornphom, K. Saenkam, S. Yotthuan, N. Vittayakorn and T. Bongkarn, Enhanced electrical and energy storage performances of Fe, Sb co-doped BNBCTS ceramics synthesized via the solid-state combustion technique, Ceramics International, 2024, Vol. 50 Issue 23, Part C, p. 51789-51803
– Impact Factor: 5.6
– Ranking: Q1
– DOI:10.1016/j.ceramint.2024.02.203
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0272884224007053
🧾Abstract
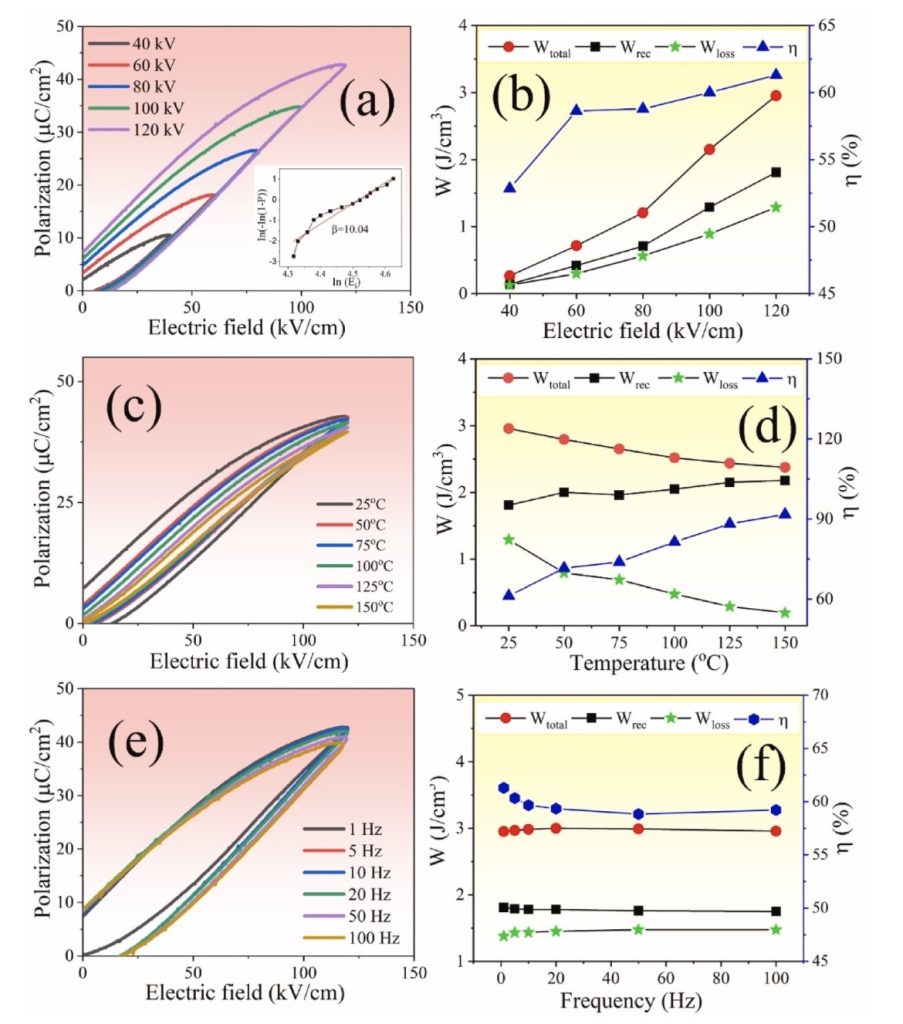
In this study BNBCTS ceramics were co-doped with Fe and Sb to form (Bi0.5Na0.5)0.93(Ba0.945Ca0.055)0.07(Ti(0.9946-x)Sn0.0054)(Fe0.5Sb0.5)xO3 ceramics (denoted as BNBCTS-xFS) with various x content and were prepared via the solid-state combustion technique to enhance the electrical and energy storage performance. The effect of co-doping Fe and Sb on the phase formation, defect dipole, microstructure, electrical and energy storage properties of BNBCTS-xFS ceramics was studied. When x content increased from 0.0 to 0.030, the amount of the rhombohedral (R) phase decreased from 51 to 24 % while the tetragonal (T) phase increased from 49 to 76 %. The increased Fe and Sb content increased the defect dipole of singly/doubly charged oxygen-vacancies and caused more Ti4+ to transition to Ti3+, which caused the transition temperature of the ferroelectric phase to relaxor state (TF-R) in the ceramics to drop to below room temperature and it exhibited relaxor characteristics at room temperature. The ceramic with an x content of 0.010 had the largest grain size (3.06 μm), excellence ferroelectric properties (Pr ∼31.04 μC/cm2, Pm ∼38.98 μC/cm2 and Ec ∼18.28 kV/cm), the largest electro strain (∼0.175 %) and a large
of 350 pm/V. Moreover, when x = 0.020, the ergodic relaxor ceramic showed the smallest grain size (1.03 μm), the lowest remanant polarization (Pr) of 4.52 μC/cm2 and the lowest coercive field (Ec) of 8.37 kV/cm, at an electric field of 60 kV/cm. More importantly, energy storage properties at the electric breakdown strength (Eb = 120 kV/cm) of the ceramics with an x content of 0.020 exhibited a recoverable energy storage density (Wrec) of 1.81 J/cm3, a total energy storage density (Wtotal) of 2.95 J/cm3 and an efficiency (η) of 61.30%, with excellent thermal (∼25–150 °C) and frequency stability (∼1–100 Hz). This study provides new insights into the modulation of BNBCTS ceramics with Fe and Sb co-doping, which could effectively improve the electrical properties and energy storage properties of BNBCTS-xFS ceramics.

🧑🔬👩🔬 ดร. สุรีรัตน์ ยอดเถื่อน ตำแหน่ง นักวิทยาศาสตร์ชำนาญการ, นส. อุษณีย์ พันธุลาภ ตำแหน่ง นักวิทยาศาสตร์ชำนาญการ, นส. ณัฐวัลคุ์ แสวงบุญ ตำแหน่ง นักวิทยาศาสตร์ปฏิบัติการ, นส. กานต์สิรี แก้วมรกต ตำแหน่ง นักวิทยาศาสตร์ปฏิบัติการ, นส. อรอุมา ตั้งสววน ตำแหน่ง นักวิทยาศาสตร์, นส. ณฐพร อุทัยชัย ตำแหน่ง นักวิทยาศาสตร์ และ ดร. เอกรัฐ มีชูวาศ ตำแหน่ง ผู้อำนวยการศูนย์ห้องปฏิบัติการอ้างอิงฟิสิกส์ (ผอ.ศอฟ.)
🔬- กลุ่มวิเคราะห์โครงสร้างและพื้นผิว (คพ.) ศูนย์ห้องปฏิบัติการอ้างอิงทางฟิสิกส์ (ศอฟ.)
📑 ผู้ร่วมวิจัย ลำดับที่ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7
Surirat Yotthuan, Usanee Pantulap, Nuttawan Sawangboon, Ornuma Tughsanguan, Ekarat Meechoowas, Kansiree Kaewmorakot, Nathaporn Uthaichai and Theerachai Bongkarn, Improving the mechanical performance of 45S5 3D scaffolds through the particles of barium titanate ceramics, Journal of Metals, Materials and Minerals, 2025, 35(3), e2308
– Impact Factor: 1.5
– Ranking: Q2
– DOI:10.55713/jmmm.v35i3.2308
https://jmmm.material.chula.ac.th/index.php/jmmm/article/view/2308/1387
🧾Abstract
Bioglass® 45S5 is widely used in bone tissue engineering due to its excellent bioactivity. However, its low mechanical strength remains a major limitation. In this study, 25 wt% barium titanate (BaTiO3; BT) was incorporated into 45S5 scaffolds to improve mechanical performance and modulate bioactivity. The 3D scaffolds were fabricated using the foam replication method and exhibited interconnected porosity, with average pore sizes of 471 ± 94 μm (45S5) and 598 ± 58 μm (45S5/BT25), closely resembling human bone. The addition of BT increased the density and compressive strength of the scaffolds to 2.89 ± 0.18 g∙cm-3 and 2.0 ± 0.2 MPa, respectively. Bioactivity evaluation in simulated body fluid (SBF) revealed delayed carbonated hydroxyapatite (CHA) formation in 45S5/BT25 scaffolds, with CHA detected after 21 days, compared to 7 days in pure 45S5. This delay was consistent with FTIR, SEM-EDS, and XRD results and is likely attributed the formation of a stable Ba2TiSi2O8 phase. Overall, these results indicate that BT-modified 45S5 scaffolds not only exhibit improved mechanical performance but also offer tunable bioactivity, making them promising candidates for tailored bone regeneration applications.


